Matplotlib Tutorial
What is Matplotlib?
Matplotlib is a low level graph plotting library in python that serves as a visualization utility.
Matplotlib was created by John D. Hunter.
Matplotlib is open source and we can use it freely.
Matplotlib is mostly written in python, a few segments are written in C, Objective-C and Javascript for Platform compatibility.
Installation of Matplotlib
If you have Python and PIP already installed on a system, then installation of Matplotlib is very easy.
Install it using this command:
install matplotlib
Import Matplotlib
Once Matplotlib is installed, import it in your applications by adding the import module statement:
import matplotlib
Now Matplotlib is imported and ready to use:
Matplotlib Pyplot
Pyplot
Most of the Matplotlib utilities lies under the pyplot submodule, and are usually imported under the plt alias:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Now the Pyplot package can be referred to as plt.
Example
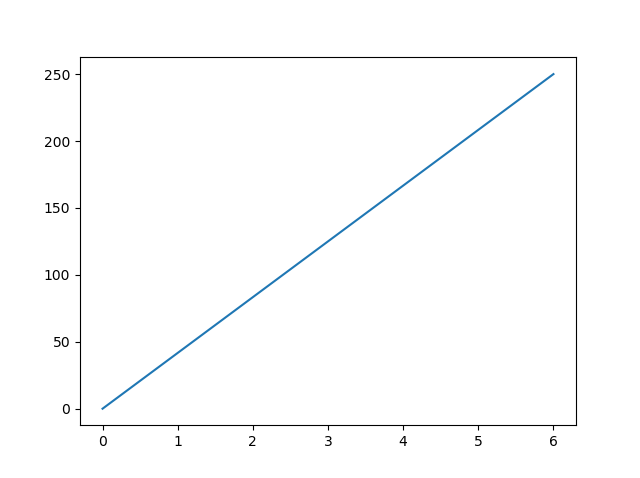
Draw a line in a diagram from position (0,0) to position (6,250):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
xpoints = np.array([0, 6])
ypoints = np.array([0, 250])
plt.plot(xpoints, ypoints)
plt.show()
Result:
Matplotlib Plotting
Plotting x and y points
The plot() function is used to draw points (markers) in a diagram.
By default, the plot() function draws a line from point to point.
The function takes parameters for specifying points in the diagram.
Parameter 1 is an array containing the points on the x-axis.
Parameter 2 is an array containing the points on the y-axis.
If we need to plot a line from (1, 3) to (8, 10), we have to pass two arrays [1, 8] and [3, 10] to the plot function.
Example
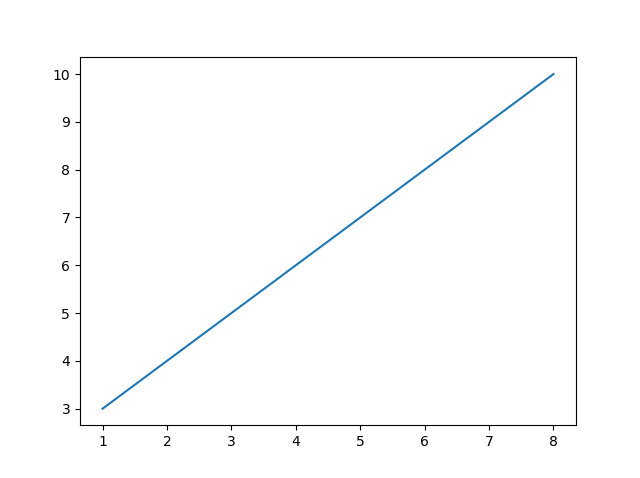
Draw a line in a diagram from position (1, 3) to position (8, 10):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
xpoints = np.array([1, 8])
ypoints = np.array([3, 10])
plt.plot(xpoints, ypoints)
plt.show()
Result:
Plotting Without Line
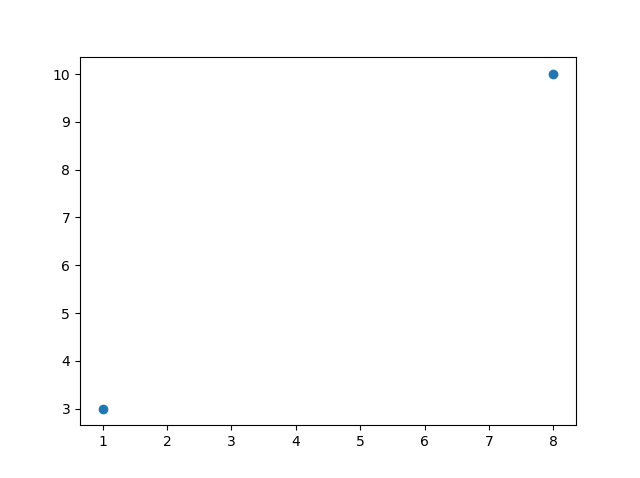
To plot only the markers, you can use shortcut string notation parameter ‘o’, which means ‘rings’.
Example
Draw two points in the diagram, one at position (1, 3) and one in position (8, 10):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
xpoints = np.array([1, 8])
ypoints = np.array([3, 10])
plt.plot(xpoints, ypoints, 'o')
plt.show()
Result:
Multiple Points
You can plot as many points as you like, just make sure you have the same number of points in both axis.
Example
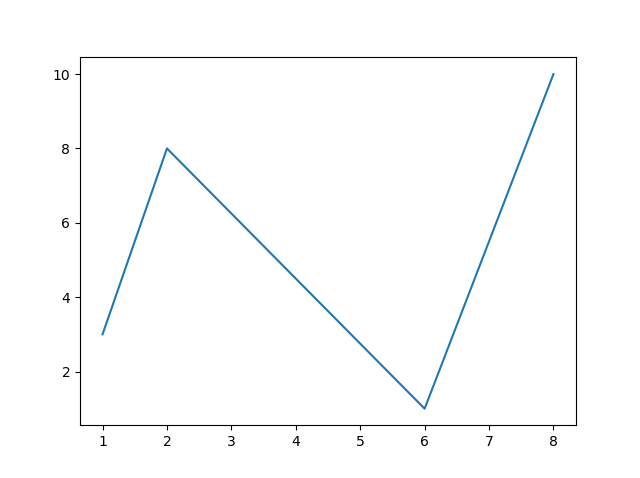
Draw a line in a diagram from position (1, 3) to (2, 8) then to (6, 1) and finally to position (8, 10):
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
xpoints = np.array([1, 2, 6, 8])
ypoints = np.array([3, 8, 1, 10])
plt.plot(xpoints, ypoints)
plt.show()
Result:
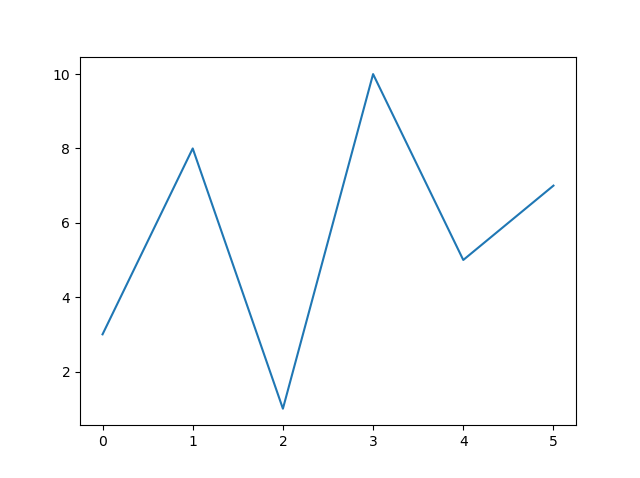
Default X-Points
If we do not specify the points in the x-axis, they will get the default values 0, 1, 2, 3, (etc. depending on the length of the y-points.
So, if we take the same example as above, and leave out the x-points, the diagram will look like this:
Example
Plotting without x-points:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
ypoints = np.array([3, 8, 1, 10, 5, 7])
plt.plot(ypoints)
plt.show()
Result: